The costs of manufacturing the pumps have also declined significantly over the last decade, which bolsters the case for heat pumps.
Heat pumps have been repeatedly identified as a key, cost-effective solution for tackling the carbon emissions associated with keeping buildings warm. The global heat pump market size is expected to expand at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2022 to 2030. If you are looking to invest in a heat pump, you are not alone — many entrepreneurs are making the switch.
Before you rush into a decision, you are suggested considering the following factors before purchasing the right for your customers or your own commercial buildings.

Heat Pump Types
The first important factor in choosing the right heat pump is choosing the right capacity, or heat pump size. The second is the location of the heat pump, which can make a big difference in the effectiveness and unobtrusiveness of the unit. All those factors fall into one question: What type of heat pump do you need?
Air-source, water-source, and ground-source are a few main types of heat pumps. Air Source technology is expected to dominate the market in the U.S. over the forecast period due to that air source is the quickest and easiest to install and it looks like a normal air conditioning unit. You can use these units to generate hot water or hot air, some units can also incorporate a reversing valve to operate in cooling mode also. The main heat pump products from Smeta are air-sourced, if you need to know the installation procedures or other requirements, you are welcome to leave your questions.
Ground source is the second most popular option, it’s more commonly used for hot water production but you can also get units and systems that can reverse to provide cooling. It uses thermal energy embedded within the ground that comes from the sun. This option requires extensive excavation however and is typically costlier to install, so it’s best suited to new builds as it can be incorporated within the construction to reduce costs.
Water-source heat pumps draw heat from a pond, lake, or water deposit, Each type has its advantages and disadvantages.

Efficiency
There are many standards used across the world for assessing the efficiency of heat pumps. I’m going to take one of the most common ones as an example, focusing on units made in the US and EU — COP:
COP values or the coefficient of performance is used worldwide for both heating and cooling, it’s simply the heating or cooling output divided by the electricity input. Basically speaking, this number is basically dollars in vs heat out. For example if a heat pump has a COP of 4.27, this means $1 electricity equates to $4.27 heat. Compare that to an oil heater where $1 electricity gets you $1 heat.We reviewed the manufacturer literature of many air source units and found them to vary between 2.75 and 6.13.
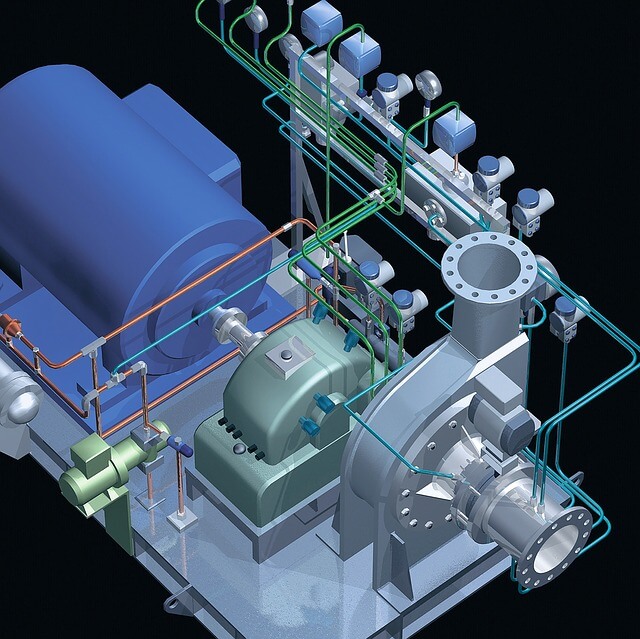
Compressor Type
The efficiency is highly related to a core component of a heat pump — the compressor. It is the primary factor that determines whether the heat pump is good or bad. What counts is not merely the energy efficiency of the compressor but also the limits placed on applications by the evaporating and condensing temperatures, highly durable mechanical parts and quiet operation. Moves the refrigerant through the system.Heat pumps manufactured by Smeta contain a scroll compressor. When compared to a piston compressor, scroll compressors are quieter, have a longer lifespan, and provide 10° to 15°F warmer air when in the heating mode. A good heat pump compressor will offer an outstanding seasonal performance factor that is kind to both natural resources and the operator’s wallet. It will also be as flexible as possible as regards evaporation and condensing temperatures and will emit no obtrusive noise. With good compressors, there will be no stopping the triumphal progress of the heat pump.
Refrigerant type
A refrigerant, also known as a cooling agent, is a thermodynamic medium involved in the process of heat exchange in a piece of cooling equipment or heat pump.
While there are currently heat pumps operating with various working media in the market, several of these may be considered the most popular.
By refrigerant type, the heat pump market is segmented into R410A, R290, R32, and others. The R410A and R290 segment holds the largest share in the market. The refrigerant can boost the system’s efficiency rating. The minimum effect on the ozone layer is expected to drive the R410A and R290 refrigerant segment of the heat pump market during the forecast period.
Those were some of the essential factors that you need to consider when looking for heat pumps. If you are interested in heat pump products, please feel free to let us know.


